

With regards to organic hydroponics (i.e. In addition, aquaponic water contains organic matter that could promote establishment and growth of heterotrophic bacteria in the system or even improve plant growth and viability directly. However, suppressive action (suppression) could happen in aquaponic environment considering recent papers and the suppressive activity already highlighted in hydroponics. Consequently, ways to control the initial infection and the progression of a disease are mainly based on preventive actions and water physical treatments. Furthermore, the development of biocontrol agents for aquaponic use is still at its beginning. In coupled aquaponics, curative methods are still limited because of the possible toxicity of pesticides and chemical agents for fish and beneficial bacteria (e.g. which belong to the Oomycetes pseudo-fungi require special attention because of their mobile form of dispersion, the so-called zoospores that can move freely and actively in liquid water. and Pythium spp., are the most problematic due to their preference for humid/aquatic environment conditions. If extensive damage appears, turf seldom responds to fungicide treatment (See the section Chemical Controls for Turfgrass Diseases).Among the diversity of plant diseases occurring in aquaponics, soil-borne pathogens, such as Fusarium spp., Phytophthora spp. Fungicide control of Pythium root rot is less consistent than control of foliar blight. During extended periods of warm, humid weather, a preventive fungicide program is advised. Increasing the mowing height and other practices that promote root growth may lessen the damage from Pythium root rot. Increase air movement by reducing shading, selective pruning or fans.
Remove thatch with frequent verticutting and avoid overfertilization.

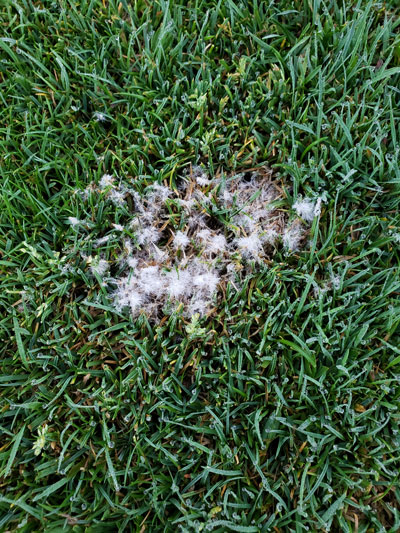
Avoid late day watering and overwatering new plantings. Symptoms of Pythium root rot mimic melting out and anthracnose and there is no foliar mycelium.Ĭontrol and Management: Diagnosis should be confirmed by a diagnostic laboratory as soon as possible. It also can cause crown and root rots which generally occur in early spring or late fall when soils are cool and excessively wet or saturated. Pythium may cause seedling blight and poor stand development in perennial ryegrass overseedings. Hybrid bermudas are more susceptible to pythium than common bermudagrass. When disease is very active, fungal mycelium grows profusely over affected plants so that diseased areas have a cotton-like appearance. On close-cut turf, pythium blight may appear as streaks that follow water drainage or mowing patterns. Roundish, dark, greasy to slimy patches of matted grass, from two to 12 inches in diameter, appear suddenly.
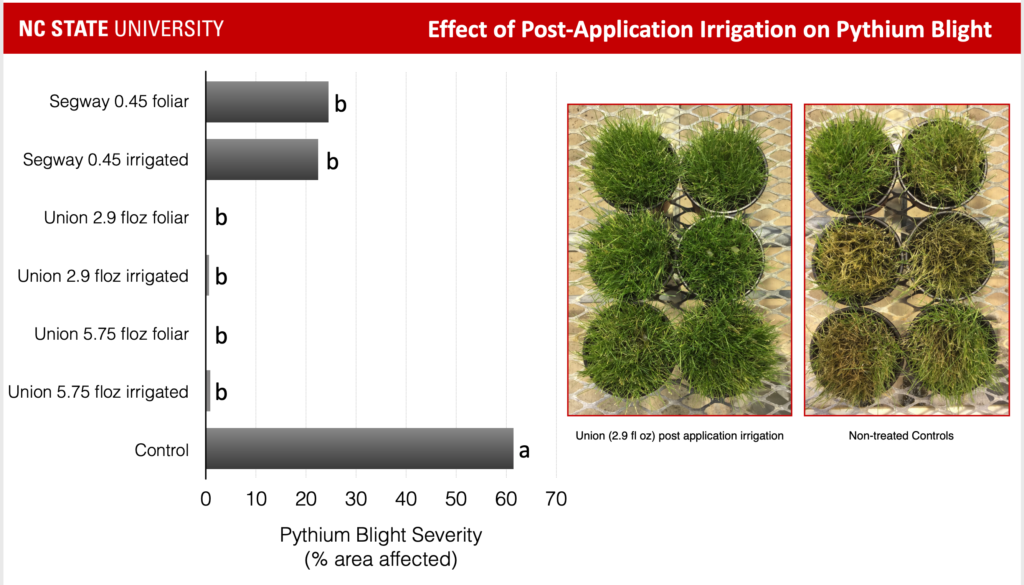
#PYTHIUM BLIGHT CONTROL SERIES#
Host Grass: Hybrid Bermuda( Cynodon dactylon), Common Bermuda, Bentgrass( Agrostis palustris), Fescue, Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne), Poa Series (Poa sp.)Ĭause and Sym p toms: Disease is favored during rainy, foggy weather and in low lying areas where air circulation is poor. Pythium Blight, Cottony Blight, Greasy Spot (fungus – Pythium aphanidermatum )


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
